What are Chain Signatures?
Chain signatures enable NEAR accounts, including smart contracts, to sign and execute transactions across many blockchain protocols.
This unlocks the next level of blockchain interoperability by giving ownership of diverse assets, cross-chain accounts, and data to every single NEAR account.
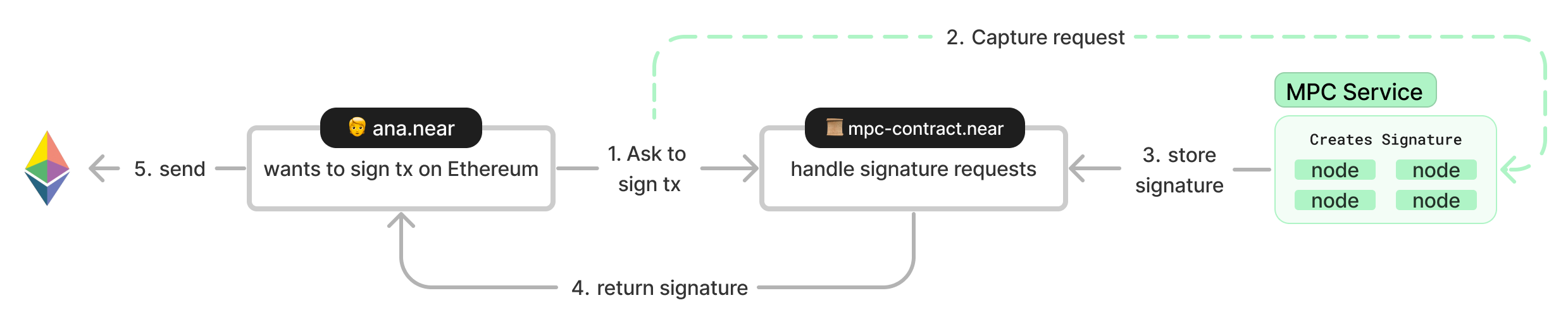 Diagram of a chain signature in NEAR
Diagram of a chain signature in NEAR
How It Works
Controlling accounts and their assets on other blockchain platforms is made possible thanks to the interaction between three elements:
- Derivation Paths - A deterministic way to derive foreign addresses from one NEAR account
- Multichain Smart Contract - Receives requests to sign a transaction for other blockchains
- Multiparty Computation Service Third-party service providing signatures to the contract
Derivation Paths: One Account, Multiple Chains
Chain Signatures link NEAR accounts to addresses in other blockchain using Additive Key Derivation (a simple mechanism for deriving many subkeys from a single master key). These keys are generated using derivation paths (or paths for short).
A derivation path is simply a string (e.g. ethereum-1, ethereum-2, etc) that in conjunction with the NEAR account derives a unique address on the target blockchain.
For example, we can derive multiple Ethereum addresses from example.near by using different paths:
example.near+ethereum-1=0x1b48b83a308ea4beb845db088180dc3389f8aa3bexample.near+ethereum-2=0x99c5d3025dc736541f2d97c3ef3c90de4d221315example.near+...=0x...
It is important to note that this allows us to discover the public address of the foreign account that we can control. To actually control the foreign account, we need to request signatures from the MPC service.
In practice, the external address is deterministically derived using the NEAR address (example.near), the path (ethereum-1) and the MPC service's public key
Multichain Smart Contract
A deployed multichain smart contract is used to request signatures for transactions on other blockchains.
This contract has a sign method that takes two parameters:
- The
payload(transaction) to be signed for the target blockchain - The
paththat identifies the account you want to use to sign the transaction.
For example, a user could request a signature to send 0.1 ETH to 0x060f1... (transaction) using the ethereum-1 account (path).
After a request is made, the sign method will yield execution waiting while the MPC signing service signs the transaction.
Once the signature is ready, the contract resumes computation and returns it to the user. This signature is a valid signed transaction that can be readily sent to the target blockchain to be executed.
Multi-Party Computation Service��
The essence of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is to enable independent parties to perform shared computations on private information without revealing secrets to each other. In practice, this system can be used with blockchain platforms to safely sign a transaction on behalf of a user without ever having to expose a private key.
NEAR's MPC service is comprised of several independent nodes, none of which can sign by itself, but instead create signature-shares that are aggregated through multiple rounds to jointly sign a transaction.
This service continuously listens for signature requests (i.e. users calling the sign method on the v1.signer smart contract) and when a call is detected the MPC service:
- Asks its nodes to jointly derive a signature for the
payloadusing the account identified by thepath - Once complete, call the
v1.signercontract to store the resultingSignature
Generally, MPC signing services work by sharing a master key, which needs to be re-created each time a node joins or leaves.
NEAR's MPC service allows for nodes to safely join and leave, without needing to re-derive a master key
Want to learn more about the mathematics that enable MPC? Check this awesome article
Concluding Remarks
Chain Signatures are a powerful tool that allows NEAR accounts to control accounts on other blockchains. This is a fundamental step towards enabling true ownership of cross-chain data and assets.
For the user, the process is made completely on chain, since they only need to make a call to a smart contract and wait for the response.
Thanks to derivation paths, a single NEAR account can control multiple accounts on different blockchains, and thanks to the MPC service, the user can be sure that nobody but themselves can request signatures for those accounts.

